Describe the Cardiac Cycle Using the Electrical Activity
Phases of cardiac cycle are. The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs whenthe heart beats.
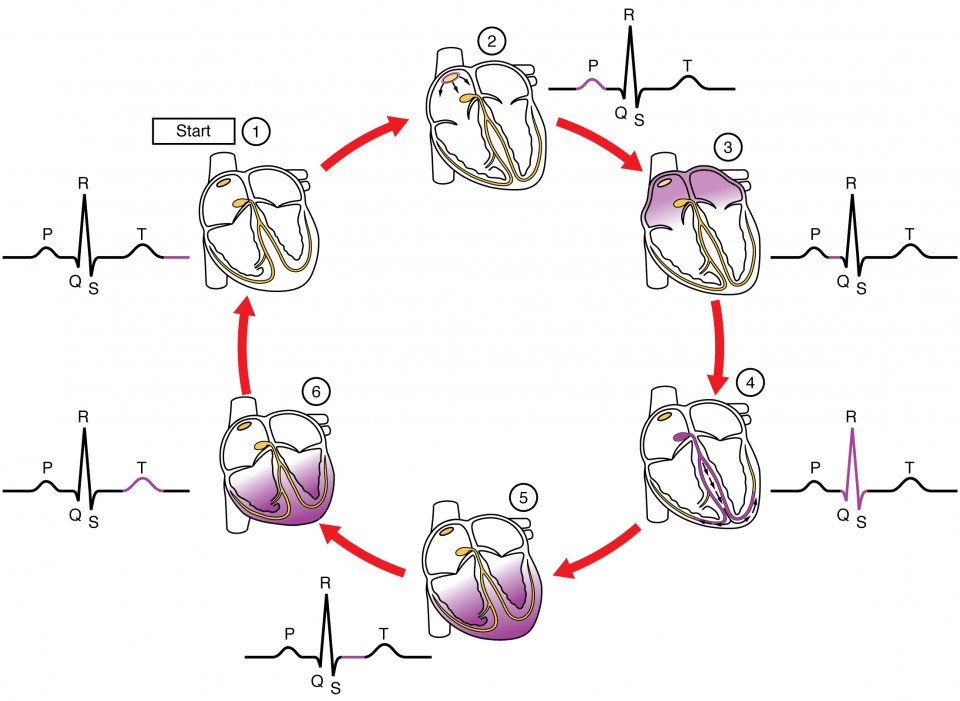
Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii
The human heart beats over 100000 times per day.

. The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. 47-4 as well as electrical activity as represented by the ECG. Describe the cardiac cycle and the associated electrical activity recorded via the electrocardiogram.
In your answer you should address. There are two phases of the cardiac cycle. AVN sends a wave of electrical activity down Bundle of His.
1 What initiates electrical activity in the heart and how is this initiation achieved. The cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways. At a heartbeat 72 beatsminute duration of each cardiac cycle will be 08 seconds.
Describe the cardiac cycle. Inthe diastole phase the heart ventricles are relaxed and theheart fill with blood. Contraction of the heart muscle is known as systole and.
Duration of different stages of the cardiac cycle is given below. View the full answer. The cardiac cycle is the repeating pattern of contraction and relaxation of the heart.
Continues for about 01 seconds. Mechanical. What prevents all four chambers.
5 Electrical Premises 1. In each cardiac cycle the heart contracts systole pushing out the blood and pumping it through the body. The period of time that begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle Figure.
Impulse for beating electrical activity of heart comes from within the heart in case of my. How would you ensure synchronous cardiac muscle contraction. What property of cardiac cells is critical for initiation of the electrical activity.
Explain the structure and function of the conduction system of the heart. Ans Cardiac cycle is the cycle of electrical and mechanical events in heart from beginning of one heart beat to other heart beat. 2 What is.
The cardiac cycle is the coordination of the filling and emptying of the heart of blood by electrical signals that cause the heart muscles to contract and relax. The Cardiac Cycle In resting humans the heart beats approximately once per second. The period of timethat begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle Figure 1931.
Atrial systole and Atrial diastole Ventricular cycle. Describe the electrical activity of the heart. First since each electrical impulse generates one heartbeat the number of electrical impulses determines the heart rate.
The ventricular diastolic stage involves blood flow from the atria to the ventricles and the ventricular systole includes blood flow from the ventricles to the pulmonary artery and the aorta. The cardiac cycle is a series of electrical and mechanical events that occur during the phases of heart relaxation diastole and contraction systole. Since the heart undergoes a series of electrical changes related to the waves of excitation sensors that are connected to a monitor can detect these electrical signals.
The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Non-conducting tissue prevents impulses reaching the ventricles.
100 2 ratings 1. The cardiac cycle is defined as a sequence of alternating contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles in order to pump blood throughout the body. AVN delays impulse whilst ventricles fill.
Cardiograms We can monitor the electrical activity of the heart using an electrocardiogram or ECG Sensors must be attached to the skin which pick up the electrical signals from the heart The trace of a healthy person has a particular shape consisting of waves labelled P Q R S and T P shows the excitation of the atria QRS indicates excitation of the ventricles T shows. Explain the importance of this short delay. The process begins as early as the 4th gestational week when the heart first begins contracting.
C When a wave of electrical activity reaches the AVN there is a short delay before a new wave leaves the AVN. The electrical event the wave of depolarization is the trigger for muscular contraction. Both the atria and ventricles undergo systole and.
In a normal person a heartbeat is 72 beatsminute. An electrocardiogram ECG is a medical device that measures the electrical pulse of the heart. What back up systems are in place incase of electrical failure of the SA node what are the consequences of using the back ups 4.
The wave of depolarization begins in the right atrium and the impulse spreads across the superior portions of both atria and then down through the contractile cells. Describe the waves of an electrocardiogram and relate each of them to contractions of the heart. Cardiac cycle Cardiac outputFilling Contraction Cardiac CycleSystoleDiastole Lub Dub 4.
Pacemaker is the SA node. Objectives Define the cardiac cycle Identify factors affecting cardiac output Describe the mechanical and electrical activityof the heart 3. SAN sends wave of electrical activity across atria causing atrial contraction.
This is followed by a relaxation phase diastole where the heart. It starts at the beginning of one heartbeat and ends at the beginning of another. Electrical Activity of the Heart.
Contract and pump blood to the arteries. Myocardial conducting cells are specialized to initiate and propagate the electrical activity that travels throughout the heart and triggers the contractions of the myocardial contractile cells that propel the blood. The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole.
_____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 2 d The table shows the cardiac output and resting heart rate of an athlete before and after completing a training programme. So the duration of one cardiac cycle can be calculated as. Describe the characteristics of action potentials in cardiac muscle.
And second as the electrical signal spreads across the heart it triggers the heart muscle to contract in the correct sequence thus coordinating each heartbeat and assuring that. With each beat the heart cycles through a series of four hemodynamic events represented by changes in pressures and volumes E-Fig. In the systole phase the ventricles.
The ECG produces a trace of electrical activity shown in Figure 6. Contraction is systole and relaxation is diastole. The cardiac cycle The cardiac cycle refers to the pattern of contraction and relaxation of the heart during one complete heartbeat.

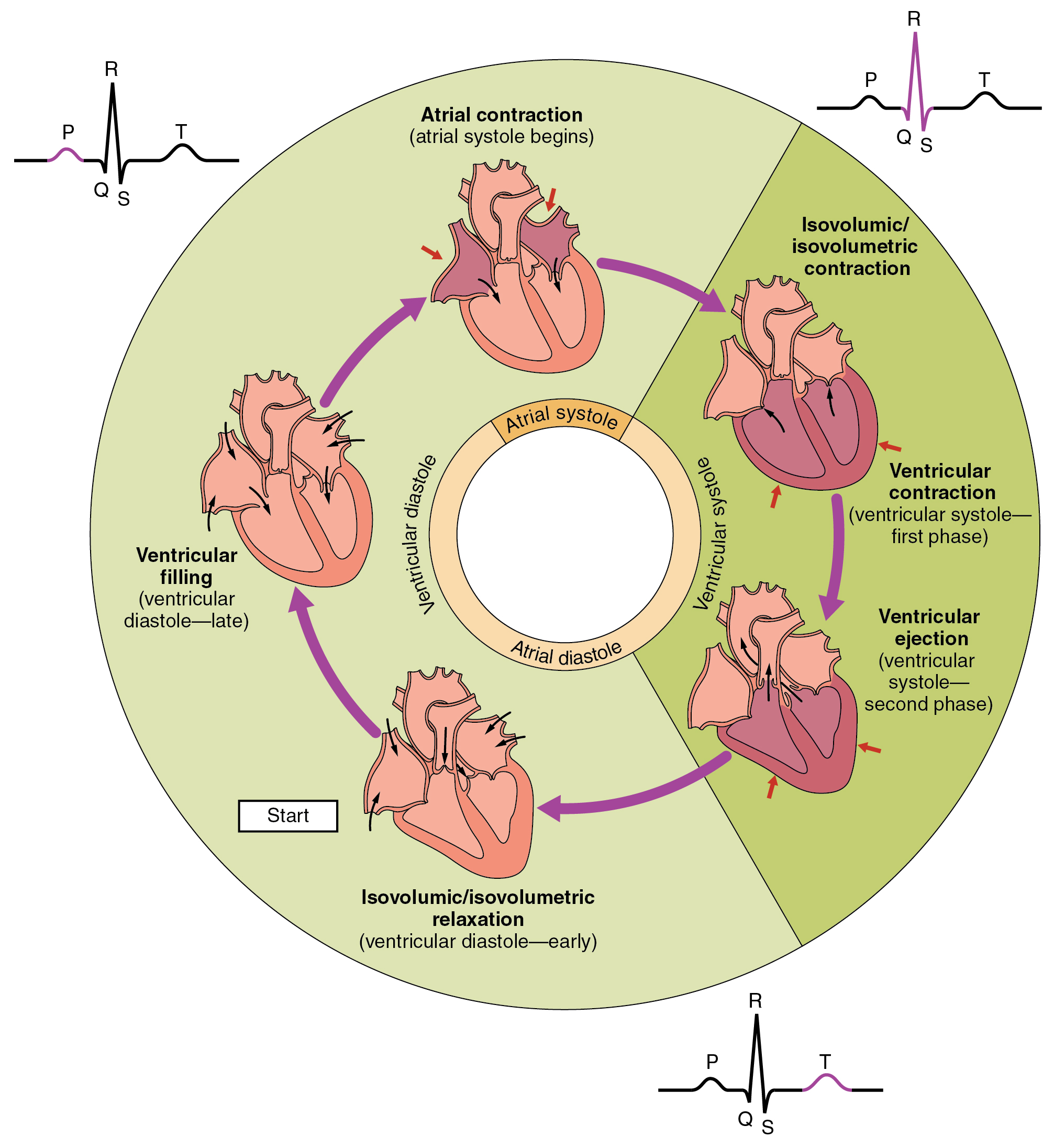
The Cardiac Cycle Biology For Majors Ii

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii
No comments for "Describe the Cardiac Cycle Using the Electrical Activity"
Post a Comment